Cyber threats are evolving faster than ever, and 2026 is shaping up to be one of the most challenging years yet for businesses of all sizes. With artificial intelligence, automation, and increasingly sophisticated social engineering techniques, cybercriminals are no longer relying on crude attacks. Instead, they are exploiting trust, human error, and visual deception.
From advanced phishing campaigns to look-alike brand scams such as the “rnicrosoft” scam, companies must rethink how they approach cybersecurity. This article explores the most critical cyber threats and scams businesses need to watch in 2026, and what organisations can do to protect themselves.
Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern. In 2026, a single breach can:
Small and mid-sized businesses are especially vulnerable. Attackers know they often lack dedicated security teams, making them prime targets for scams and ransomware.
The most dangerous trend? Attacks that look legitimate.
Traditional phishing emails were often easy to spot due to poor grammar or suspicious formatting. In 2026, that’s no longer the case.
Attackers scrape data from LinkedIn, company websites, and data breaches to craft believable messages that bypass both spam filters and human suspicion.
SEO keywords: AI phishing attacks, business email compromise, phishing scams 2026
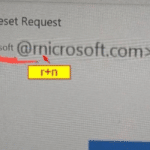
One of the most dangerous scams in 2026 is also one of the simplest: the “rnicrosoft” scam.
The scam exploits a visual trick where the letters “r” and “n” appear together as “m” in certain fonts. As a result:
Attackers use this trick to impersonate Microsoft in emails, login pages, invoices, and software update alerts.
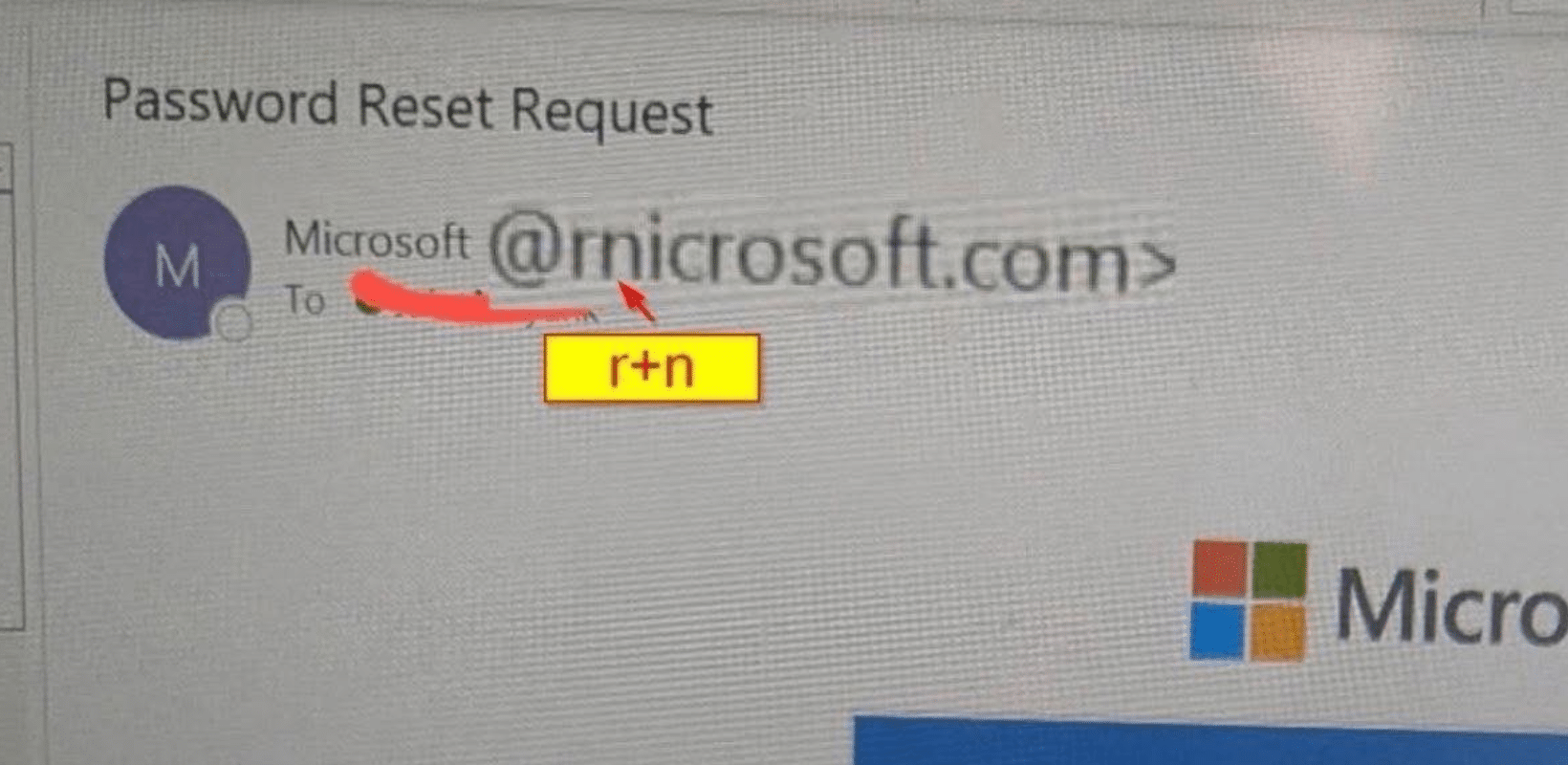
You can see this particular scam in the photo above.
The “rnicrosoft” scam is part of a much larger trend: look-alike domain attacks.
In 2026, attackers register domains that differ by:
Examples:
This is especially dangerous in invoice fraud and payment redirection scams.
Deepfake technology has advanced dramatically, and in 2026 it is being actively used in cybercrime.
These attacks prey on urgency and authority, making employees hesitate to question them.
Ransomware attacks in 2026 are no longer random. Attackers:
Many attacks now exploit:
Small companies are often targeted because attackers assume weaker defenses.
Instead of attacking a company directly, cybercriminals increasingly target:
Once compromised, attackers gain access to multiple businesses at once.
This makes vendor risk management a top priority for 2026.
Despite advanced tools, human error remains the #1 cause of breaches.
Common mistakes include:
The “rnicrosoft” scam works precisely because it exploits this trust.
Security awareness training must now include:
Even if credentials are stolen, MFA can stop attackers.
Focus on:
Companies should:
Any payment or sensitive request should be verified via:
Never rely solely on email or voice messages.
Many attacks succeed simply because patches were delayed.
Regular updates reduce exposure to:
In 2026, cybersecurity is no longer just about firewalls and antivirus software. It’s about awareness, verification, and scepticism.
Scams like the ‘rnicrosoft’ scam prove that attackers don’t always need advanced malware sometimes all they need is a clever visual trick and a moment of inattention.
Companies that invest in employee education, strong authentication, and proactive monitoring will be far better positioned to survive the evolving cyber threat landscape.