Discover what a private cloud is, its benefits, and how it boosts security, scalability, and performance for your business.
One IT solution that has gained increasing popularity is the private cloud. But what exactly is it, and why should your business consider adopting it? This guide will explore what a private cloud is, its benefits, use cases, and how it can help your business thrive.
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated exclusively to a single organisation. RevolutionCloud is a platform built with the future in mind. Silver Lining can deliver RevolutionCloud as an end-to-end private cloud or hybrid solution, ensuring maximum security at all levels.
Unlike public clouds, where resources are shared among multiple companies, private clouds offer businesses complete control over their IT infrastructure, whether on-premises or through a third-party provider. Also referred to as IaaS, Infrastructure as a Service.
Private Cloud vs Public and Hybrid Cloud:
Private clouds are particularly advantageous for businesses that handle sensitive data, work in regulated industries, or have high-volume workloads, offering a combination of security, compliance, and scalability that public solutions cannot match.
One of the primary reasons businesses adopt private clouds is for enhanced security. With a dedicated environment, companies can control who accesses data, how it’s stored, and how it’s protected. Private cloud can make it easier for an organisation to customise its resources to meet specific IT requirements.
Private clouds also simplify compliance with industry standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, thereby reducing the risk of fines or data breaches.
Example: A healthcare provider can securely store patient records while adhering to strict legal requirements, ensuring both compliance and peace of mind.
Private clouds provide dedicated resources, which translates into faster processing, consistent uptime, and predictable performance. This ensures that critical business applications run smoothly, even during periods of peak usage.
Example: A financial services firm processing high volumes of transactions can maintain reliability and avoid costly downtime thanks to a dedicated private cloud environment.
A private cloud can grow with your business. You can scale storage, processing power, and applications as your needs change, without compromising security or performance.
Example: An e-commerce business can handle seasonal traffic spikes without slowing down operations, maintaining a seamless shopping experience for customers.
While private clouds often require a higher initial investment than public clouds, they can deliver significant cost savings over time. Reduced downtime, optimised resource usage, and improved efficiency can make private clouds more economical in the long run.
Example: A telecom company that invested in a private cloud experienced a 30% reduction in IT maintenance costs within the first year, thanks to streamlined infrastructure management.
Private clouds allow businesses to customise their IT environment to meet specific needs, from security protocols to software configurations and networking setups.
Example: A financial firm can implement stricter data security measures to protect sensitive transactions, while a marketing agency may prioritise faster processing for large media files.
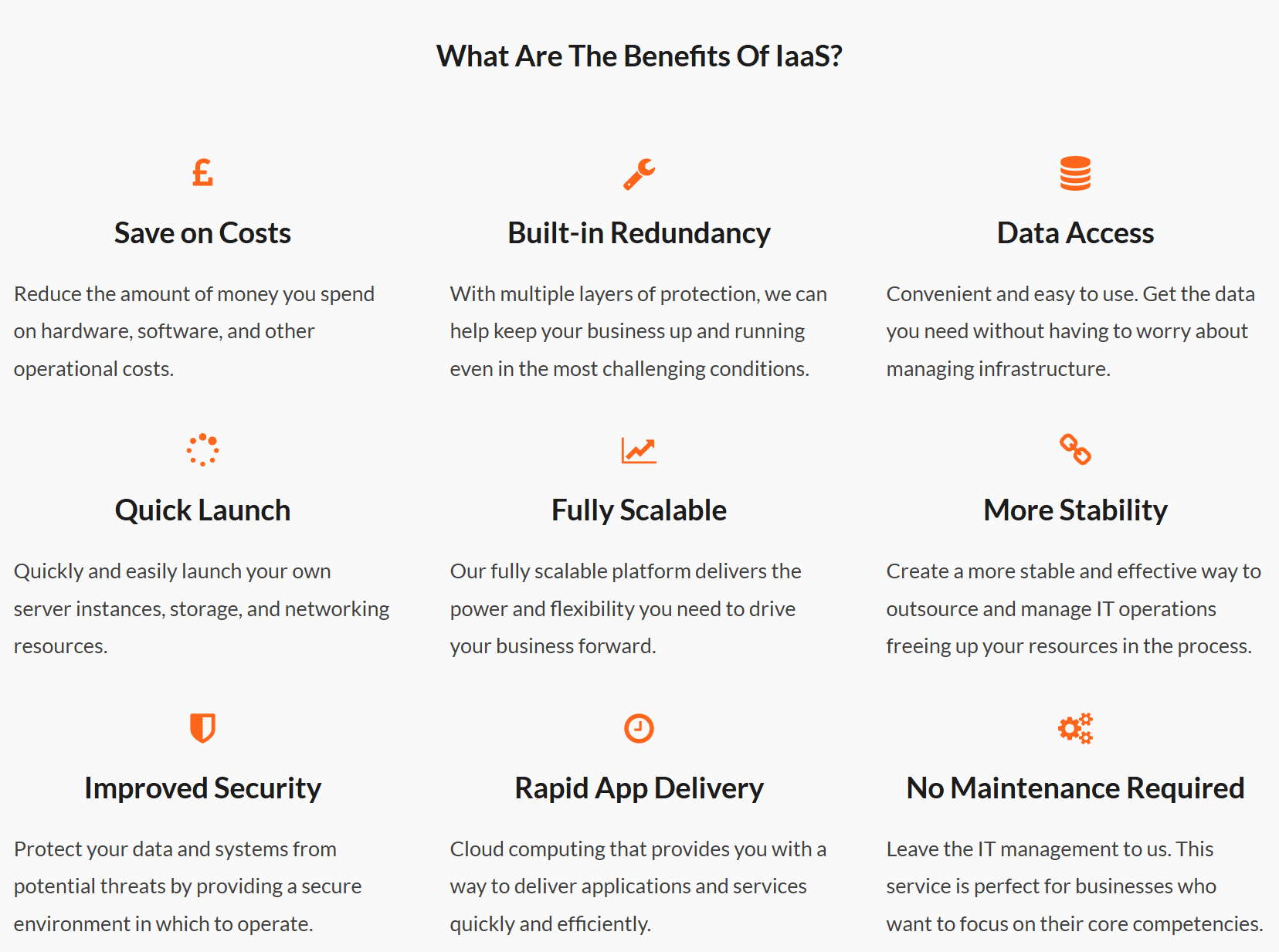
Healthcare: Secure storage of patient data, HIPAA compliance, and disaster recovery.
Finance: Transaction security, regulatory compliance, and high-speed processing.
Telecoms: Managing large-scale networks, improving uptime, and supporting cloud-based services.
E-commerce: Handling high traffic, scaling infrastructure, and improving customer experience.
By tailoring private cloud solutions to specific industries, businesses can maximise efficiency, security, and scalability.
When selecting a private cloud provider, consider the following:
Example: A UK telecom provider migrated to a private cloud, reducing downtime by 30% and improving customer service efficiency, thanks to careful selection of a provider that offered managed services and strong integration support.
Q1: Is a private cloud suitable for small businesses?
Yes, SMEs that handle sensitive data or require reliable IT performance can benefit significantly from private clouds.
Q2: How is private cloud different from public cloud?
In a private cloud, a single organisation controls and maintains the underlying infrastructure to deliver the IT resources. In a public cloud, external cloud providers provide the resources as a fully managed service.
Q3: Is private cloud expensive?
While private clouds typically have higher upfront costs than public clouds due to the dedicated resources they require, they can still offer significant savings compared to traditional on-premises software and infrastructure.
Q4: What are the 4 types of private clouds?
There are four main types of private clouds, including on-premises private cloud, virtual private cloud, hosted private cloud, and managed private cloud. These types of private cloud environments differ from each other depending on who manages the environment and where it is hosted.
Q5: Who can access a private cloud?
Companies can secure all their data with a virtual private cloud. That's because only those within the company have access.
A private cloud is more than an IT upgrade; it’s an investment in your business’s efficiency, security, and growth. With the right solution, your company gains control, reliability, and peace of mind.
At Silver Lining, we help businesses implement private cloud solutions tailored to their needs, combining security, flexibility, and performance.
Please contact Silver Lining today to discover how a private cloud can enhance your business operations.