The landscape of cyber threats is evolving rapidly, and organisations across the UK are finding themselves increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. Cyber training has become essential for businesses of all sizes, yet many companies still underestimate the critical importance of security awareness training for their workforce.
Every day, British organisations face an unprecedented volume of cyber attacks. From ransomware campaigns targeting critical infrastructure to sophisticated phishing attempts aimed at stealing sensitive data, the threat landscape continues to expand at an alarming rate.
The statistics paint a concerning picture. Research shows that human error remains the leading cause of data breaches, accounting for over 95% of successful cyber attacks. This isn't because employees are careless, it's because they lack the cyber security awareness necessary to recognise and respond appropriately to modern threats.
The Rising Cost of Cyber Incidents
When organisations experience a security breach, the financial impact extends far beyond the initial attack. Consider these factors:
Professional cyber security training programmes must address multiple areas of risk to provide comprehensive protection. Here's what truly practical training courses should include:
Security Awareness Training Fundamentals
Every training programme should begin with foundational security awareness training that helps staff recognise common threats. This includes understanding the psychology behind social engineering attacks and developing the critical thinking skills necessary to evaluate suspicious communications.
Phishing Recognition and Response
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent attack vectors, with criminals constantly refining their techniques to bypass traditional security measures. Practical training courses use realistic phishing simulations to help employees develop the instincts needed to identify suspicious emails before clicking malicious links or downloading harmful attachments.
Information Security Best Practices
Staff awareness training should cover practical information security measures that employees can implement in their daily work. This includes proper password management, secure file-sharing protocols, and understanding the importance of keeping software and systems up to date.
Incident Response Procedures
When security incidents occur, rapid response can significantly reduce the overall impact. Training programmes should ensure all staff understand their role in incident response, including who to contact, what information to preserve, and how to contain potential threats.
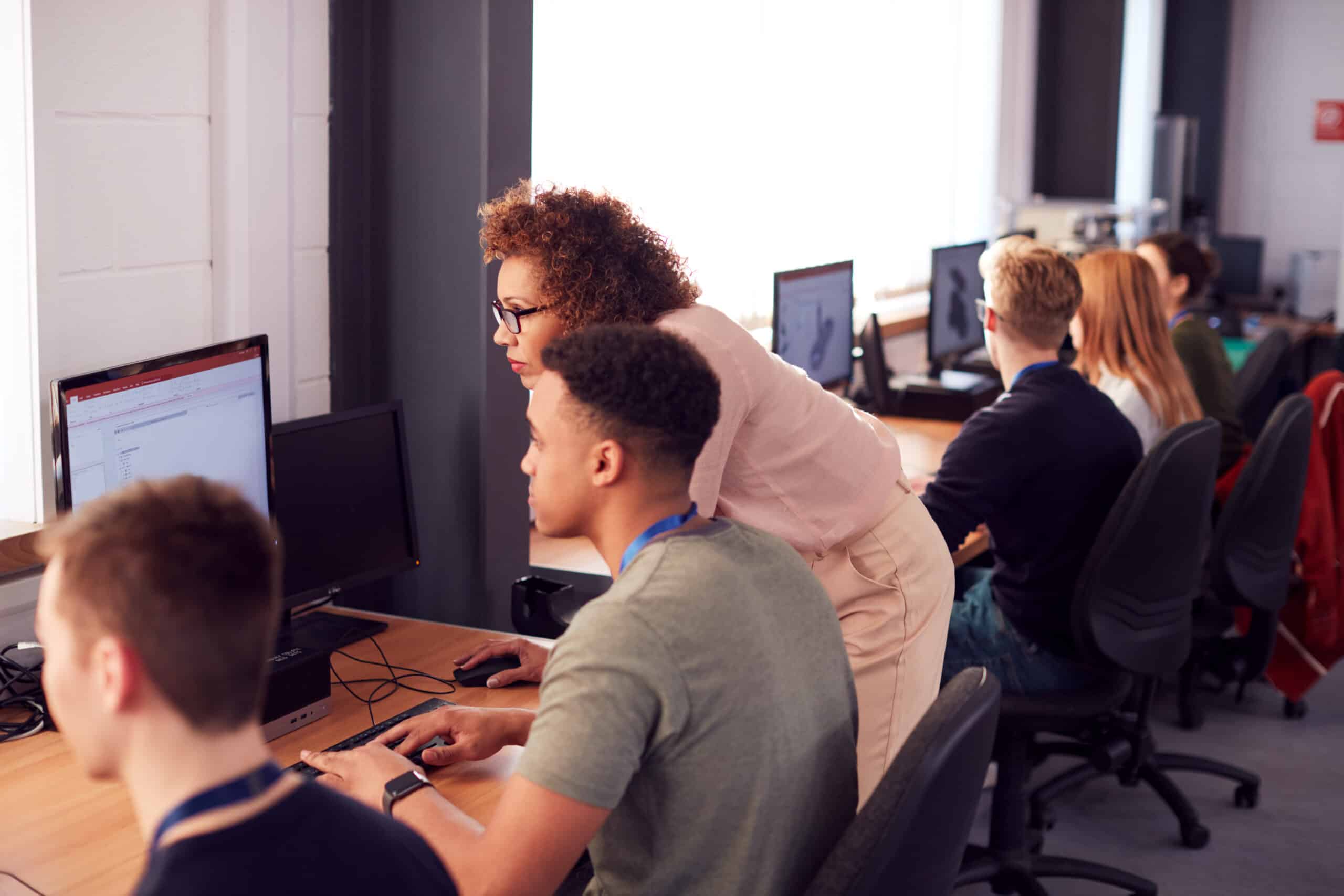

Cyber resilience isn't built through one-off training sessions. It requires ongoing education and regular reinforcement of security principles. The most successful organisations implement comprehensive training solutions that include:
Regular Training Programme Updates
The cyber threat landscape evolves constantly, with new attack methods emerging regularly. Training content must be refreshed frequently to address emerging threats and changing attack patterns. Monthly security updates and quarterly refresher training help maintain high levels of security awareness across the organisation.
Behavioural Change Through Practical Exercise
Effective cyber awareness training goes beyond theoretical knowledge to focus on changing actual behaviour. This means using interactive training content, realistic scenarios, and hands-on exercises that help staff develop practical skills they can apply immediately.
Organisational Security Culture Development
Building a strong security culture requires leadership commitment and consistent messaging throughout the organisation. When senior management actively participates in training programmes and demonstrates commitment to cyber security, it reinforces the importance of security awareness training for all staff.
Enhancing the skills of current employees bridges the technology skills gap and enables businesses to proactively respond to emerging threats, such as those driven by AI.
Advanced Persistent Threats
Modern cyber attacks often involve long-term infiltration strategies where criminals establish persistent access to organisational systems. Staff awareness training should help employees understand how seemingly innocent requests for information might be part of larger reconnaissance efforts.
Supply Chain Attacks
Cyber criminals increasingly target trusted relationships between organisations to gain access to primary targets. Training programmes should address the risks associated with third-party communications and help staff verify the authenticity of requests from suppliers, partners, and service providers.
Mobile and Remote Work Security
The shift toward flexible working arrangements has created new vulnerabilities that require specific attention in training courses. Employees need to understand the security implications of working from various locations, using personal devices, and accessing company systems over potentially unsecured networks.
Data protection regulations add another layer of complexity to cyber security training requirements. Training programmes must address both technical security measures and legal compliance obligations under the General Data Protection Regulation.
Understanding Data Protection Responsibilities
Every employee who handles personal data must understand their individual responsibilities under GDPR. This includes knowing what constitutes personal data, understanding lawful bases for processing, and recognising when data protection impact assessments may be required.
Breach Notification Procedures
GDPR requires organisations to report qualifying data breaches to the Information Commissioner's Office within 72 hours. Training programmes should ensure staff understand how to identify potential breaches and follow proper escalation procedures to meet regulatory timelines.
Privacy by Design Principles
Modern training courses should incorporate privacy by design principles, helping employees understand how data protection considerations should influence their daily work activities and decision-making processes.
Creating an effective cyber security education programme requires careful planning and consideration of organisational needs, risk profile, and existing security measures.
Assessment and Risk Analysis
Before implementing any training programme, organisations should conduct thorough risk assessments to identify specific vulnerabilities and training requirements. This includes evaluating current staff awareness levels, reviewing historical security incidents, and understanding industry-specific threats.
Customised Training Content Development
Generic training solutions rarely address the specific needs of individual organisations. The most effective programmes use customised training content that reflects actual business processes, systems, and threat scenarios relevant to the specific organisational context.
Multi-Modal Learning Approaches
Different employees learn in different ways, and effective training programmes accommodate various learning preferences through multiple delivery methods. This might include online cyber security modules, instructor-led workshops, interactive simulations, and practical exercises.
Successful training programmes include robust measurement and evaluation components to ensure ongoing effectiveness and continuous improvement.
Key Performance Indicators
Organisations should track specific metrics to evaluate training programme success:
Regular Assessment and Testing
Ongoing assessment helps identify knowledge gaps and reinforces learning objectives. This includes periodic knowledge testing, practical simulations, and scenario-based exercises that evaluate real-world application of training concepts.
Feedback Integration and Programme Refinement
Effective training programmes incorporate feedback from participants, security teams, and business stakeholders to continuously refine content and delivery methods. Regular programme reviews ensure training remains relevant and addresses emerging organisational needs.
Modern training programmes benefit from sophisticated technology platforms that support the delivery, tracking, and management of security education initiatives.
Learning Management System Features
Comprehensive learning management systems provide the infrastructure necessary to deliver, track, and manage security training across large organisations. Key features include automated course delivery, progress tracking, compliance reporting, and integration with existing HR systems.
Behavioural Analytics and Reporting
Advanced training platforms use behavioural analytics to identify patterns in employee responses to security scenarios. This data helps organisations understand which training approaches are most effective and where additional reinforcement may be needed.
Integration with Security Tools
The most effective training programmes integrate with existing security infrastructure to provide contextual learning opportunities. This might include incorporating real threat intelligence into training scenarios or using actual security incidents as case studies for learning purposes.
Practical cyber training creates lasting competency that extends beyond individual knowledge to encompass organisational capability and resilience.
Career Development and Professional Growth
Organisations that invest in comprehensive cyber security education often find that employees develop deeper interest in security careers. This can lead to internal career development opportunities and help address the broader skills shortage in the cyber security profession.
Cross-Functional Security Knowledge
Modern threats require response capabilities that span multiple business functions. Training programmes should help employees understand how security considerations relate to their specific roles whilst also developing appreciation for broader organisational security objectives.
Innovation and Adaptation Capabilities
The most successful training programmes don't just teach employees what to do; they develop critical thinking skills that enable adaptive responses to new and evolving threats. This capability becomes increasingly important as the threat landscape continues to evolve.
How often should organisations conduct security awareness training?
Best practice recommends annual comprehensive training supplemented by monthly micro-learning sessions and quarterly practical exercises. The National Cyber Security Centre suggests more frequent training for high-risk roles and following significant security incidents.
What makes cyber security training effective for non-technical staff?
Effective training for non-technical employees focuses on practical recognition skills rather than technical details. Interactive content, real-world scenarios, and clear action steps help staff understand their role in organisational security without requiring technical expertise.
How can organisations measure return on investment for security training?
ROI measurement should consider both direct costs avoided (incident response, regulatory fines, downtime) and indirect benefits (increased productivity, improved customer confidence, reduced insurance premiums). Many organisations see measurable improvements in security metrics within 3-6 months of implementing comprehensive training programmes.
What role does leadership play in successful training programmes?
Leadership commitment is essential for training programme success. When senior management actively participates in training and consistently reinforces security messaging, it demonstrates organisational commitment and encourages employee engagement with security objectives.
How should training programmes address remote and hybrid working arrangements?
Remote work training should address specific risks, including home network security, device management, physical security considerations, and secure communication practices. Training content should provide practical guidance for maintaining security across various work environments.
What training solutions work best for small and medium enterprises?
SMEs often benefit from online training solutions that provide professional content without requiring significant internal resources. Cloud-based learning management systems and managed training services can provide enterprise-level capabilities at scale appropriate for smaller organisations.
The cyber threat landscape will continue to evolve, but organisations that invest in comprehensive training programmes position themselves to adapt and respond effectively to emerging challenges. Professional cyber security training isn't just about compliance or risk management; it's about building organisational capability that supports long-term business success.
Effective training programmes require ongoing commitment, adequate resources, and leadership support. However, the investment in building cyber security awareness and competency pays dividends through reduced risk, improved operational resilience, and enhanced organisational reputation.
Don't wait for a security incident to highlight the importance of proper training. Start building your organisation's cyber resilience today through comprehensive security awareness training that prepares your workforce to recognise, respond to, and help prevent cyber attacks.
Discover our comprehensive security awareness training programmes designed to build lasting cyber resilience, or explore our complete range of cyber security solutions tailored for UK businesses.